Archaeological Endeavors: Illuminating the Enigmatic Historical Landscape of Ancient India.
Archaeological exploration plays a pivotal role in unraveling the intricate tapestry of ancient India’s history. Through systematic excavation, comprehensive analysis, and insightful interpretation, proficient archaeologists breathe life into historical records, shedding light on the opulent cultural heritage of the vast subcontinent. This article embarks on a compelling journey, delving into the array of archaeological sources scattered across India’s terrain. It uncovers the meticulous methods employed in their discovery and preservation, revealing their profound significance in understanding the long-forgotten civilizations that once thrived on this sacred land.
Diverse Categories of Archaeological Sources:
Excavated Sites:
These are physical locations where archaeological remnants are unearthed through methodical digging and exploration. Remarkable excavated sites lay bare the vestiges of ancient civilizations, offering a treasury of knowledge. Noteworthy locations in India encompass Mohenjo-daro and Harappa, relics of the Indus Valley Civilization, the historic city of Taxila, and the revered Buddhist enclave of Sanchi. Through intricate stratigraphic examination and contextual analysis of unearthed artifacts, adept archaeologists ingeniously assemble fragments of bygone eras, providing insights into daily life, urban structures, and societal frameworks.

2. Inscriptions and Epigraphs:
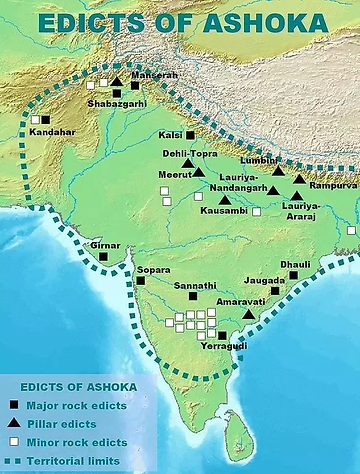
These are texts carved or engraved onto surfaces such as stone, metal, or clay. These historical inscriptions often harbor invaluable information concerning religion, administration, and history. Examples such as the Ashoka pillars and Emperor Ashoka’s rock edicts offer glimpses into the political and spiritual ideologies of ancient India. Epigraphs found on temple walls and within caves provide insights into artistic and linguistic traditions of diverse epochs.
3. Coins and Currency:
Coins and currency constitute significant archaeological sources for comprehending the economic systems, trade networks, and monetary practices of ancient India. Coins from various dynasties, including the Mauryan, Gupta, and Kushan empires, serve as compelling records of regional and international commerce. Adorned with symbols, inscriptions, and meticulously crafted images, these numismatic artifacts are vital in identifying rulers, dynasties, and the cultural currents that shaped them.

4. Artifacts and Pottery:
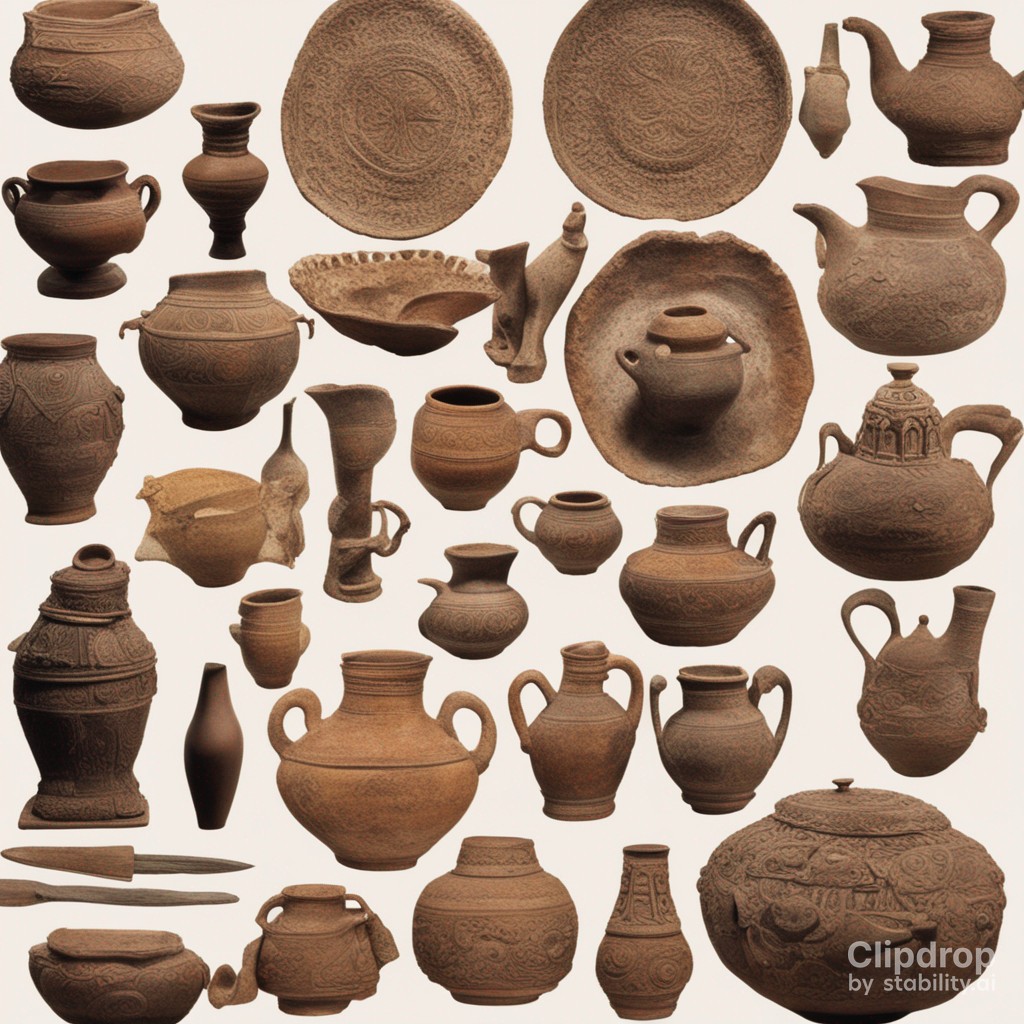
Artifacts and pottery divulge insights into the material culture, artisanal craftsmanship, and artistic expressions of ancient India. These artifacts encompass tools, weaponry, jewelry, and domestic items. Particularly, pottery serves as a chronological gauge, revealing trade patterns, regional distinctions, and technological progress. Distinctive designs and styles of pottery discovered at various sites contribute to understanding regional traditions and advancements in technology.

5. Sculptures and Monuments:
Sculptures and monuments emerge as prominent archaeological resources, offering insights into the religious, artistic, and architectural facets of ancient India. Intricately carved sculptures found in temples, caves, and monastic enclaves showcase the mastery and devotion of artisans. Illustrations include the awe-inspiring sculptures of Ellora and Khajuraho temples, portraying deities, mythological sagas, and everyday scenes. These sculptures are pivotal in grasping the spiritual beliefs, iconography, and societal norms of that era.

6. Cave Paintings and Rock Art:
Prehistoric artworks adorning caves, shelters, and rocky surfaces throughout India provide a captivating glimpse into antiquity. The Bhimbetka rock shelters in Madhya Pradesh house some of the world’s oldest rock paintings, dating back millennia. These masterpieces serve as priceless windows into the rituals, lifestyles, and cultural practices of early human societies.

7. Literary and Historical Texts:
Literary and historical texts, such as the Vedas, Upanishads, and the Ramayana, hold paramount archaeological value in understanding ancient India. Written in Sanskrit and other languages, these texts encapsulate intricate narratives encompassing religious beliefs, philosophical concepts, societal norms, and historical events. They offer profound insights into the rich tapestry of yesteryears.

Intricacies of Human and Natural Remains
i. Human Remains:
Human remains, including skeletons and burial sites, provide invaluable insights into ancient populations, demographics, health conditions, and burial practices. Bioarchaeological studies of skeletal remains yield information about the diet, diseases, and physical activities of ancient people, contributing to our understanding of population movements, interactions, and genetic diversity in ancient India.
ii. Natural Remains:
Natural remains, including fossils, flora, and fauna, are significant archaeological sources that help reconstruct ancient environments and understand the ecological context of ancient India. Fossilized remains found in sedimentary deposits provide information about past climates, vegetation, and animal species. Pollen analysis and botanical studies shed light on ancient agricultural practices, plant biodiversity, and the impact of human activity on the environment.
Sources of Ancient Indian History PDF
Methodologies and Techniques in Archaeological Pursuits
1. Excavation:
Excavation stands as a cornerstone technique in archaeology. It entails meticulously removing layers of soil and debris to unveil archaeological remnants. Archaeologists adhere to systematic protocols and meticulous recording to conserve the stratigraphic context of artifacts and structures. By examining spatial connections and associations within the excavation site, researchers construct chronological sequences of events and fathom the purpose and importance of distinct features.
2. Dating Techniques:
Dating techniques wield pivotal roles in establishing the chronology of archaeological sites and artifacts. Radiocarbon dating, relying on the decay of carbon-14 in organic material, extensively aids in determining the age of bones, charcoal, and plant fibers.
3. Preservation and Conservation:
The preservation and conservation of archaeological sites, artifacts, and monuments are vital endeavors. Conservation encompasses stabilizing and restoring fragile objects with specialized materials and methods. Preservation aims to thwart deterioration and damage via controlled environmental conditions, proper storage, and thorough documentation. Both facets secure the longevity and accessibility of archaeological sources for posterity.
The Significance of Archaeological Sources in Decoding Ancient India
Archaeological sources stand as invaluable conduits for reconstructing the past and comprehending the culture of ancient India. They proffer tangible evidence that complements the information furnished by textual sources. Through the amalgamation of archaeological and historical data, researchers attain a more holistic grasp of ancient civilizations. These sources significantly enrich our understanding of ancient India in various key domains:
- Reconstructing ancient civilizations: Archaeological sources facilitate the reconstruction of ancient societies, unveiling social, political, and economic frameworks.
- Illuminating economic systems and trade routes: By scrutinizing coins, trade commodities, and historical marketplaces, archaeologists decipher the economic systems and commercial interchanges of ancient India. The revelation of ancient ports such as Lothal and Muziris sheds light on maritime trade routes.
- Unveiling religious and cultural practices: Temples, sculptures, and religious artifacts offer insights into the spiritual convictions, rituals, and artistic expressions of ancient Indians. The exploration of sacred sites and religious iconography aids in understanding the varied religious traditions that thrived in ancient India.
- Investigating technological advancements and artistic accomplishments: Artifacts and architectural remnants unveil the technological prowess and artistic feats of ancient Indian civilizations. The use of iron implements, advancements in pottery methods, and intricate craftsmanship in sculpture and jewelry highlights the innovative spirit and artistic brilliance of that era.
Challenges in the Realm of Archaeological Research
Despite the wealth of knowledge provided by archaeological sources, researchers encounter several challenges in their pursuit of enlightenment. These challenges encompass:
1. Preservation and Site Management:
Archaeological sites confront threats from natural calamities, urban development, and human activities.
Safeguarding and managing these sites necessitate continuous endeavors, sufficient funding, and collaboration between archaeologists, government entities, and local communities.
2. Deciphering Ancient Scripts and Languages:
Numerous ancient inscriptions and texts in India are inscribed in scripts and languages that are no longer in common use. Decoding ancient scripts, such as Brahmi, Kharosthi, and Tamil-Brahmi, presents difficulties; however, their investigation furnishes invaluable insights.
3. Fragmentary Nature of Archaeological Evidence:
Archaeological evidence, though often fragmented or incomplete, requires meticulous analysis and interpretation, accounting for the constraints imposed by absent or damaged artifacts, structures, or inscriptions.
4. Ethical and Legal Considerations:
Ethical and legal considerations wield significant influence in archaeological research, particularly concerning the excavation, ownership, and repatriation of cultural artifacts. Balancing the pursuit of knowledge with the preservation of cultural heritage and respecting the rights and sentiments of local communities stands as paramount.
The Unveiling of Ancient India’s Narrative through Archaeological Sources
Archaeological sources serve as windows to the past, unveiling the intricacies and complexities of ancient India. Unearthed sites, inscriptions, coins, artifacts, sculptures, cave paintings, literary texts, human remains, and natural remnants collectively contribute to comprehending the diverse cultural legacy of the subcontinent. By employing scientific methodologies, safeguarding archaeological sites, and adhering to ethical considerations, researchers continue to uncover the untold tales of ancient India, ensuring that this invaluable wisdom remains accessible to future generations.
Archaeological Sources of Ancient India FAQs
1. What are the archaeological sources of ancient Indian history?
The archaeological sources of ancient Indian history are the physical remains of the past that are excavated by archaeologists. These sources include excavated sites, inscriptions, coins, artifacts, sculptures, cave paintings, literary texts, human remains, and natural remains.
2. What are the different types of archaeological sources?
The different types of archaeological sources are:
Excavated sites: These are physical locations where archaeological remains are unearthed through systematic digging and exploration.
Inscriptions and epigraphs: These are writings carved or engraved on various surfaces such as stone, metal, or clay.
Coins and currency: These serve as valuable archaeological sources for understanding ancient India’s economic systems, trade networks, and monetary practices.
Artifacts and pottery: These are objects made by humans that can provide information about their culture, technology, and lifestyle.
Sculptures and monuments: These can provide information about the art, architecture, and religion of ancient India.
Cave paintings and rock art: These can provide insights into the beliefs, rituals, and daily life of ancient people.
Literary texts: These can provide information about the political, social, economic, and cultural history of ancient India.
Human remains: These can provide information about the diet, health, and lifestyle of ancient people.
Natural remains: These can provide information about the climate, environment, and natural resources of ancient India.
3. What are the most important archaeological sources of ancient Indian history?
The most important archaeological sources of ancient Indian history are the excavated sites of the Indus Valley Civilization, the Mauryan Empire, and the Gupta Empire. These sites have yielded a wealth of information about the material culture, political history, and religious beliefs of these civilizations.
4. How do archaeological sources help us understand ancient Indian history?
Archaeological sources help us understand ancient Indian history by providing us with physical evidence of the past. This evidence can be used to reconstruct the material culture, political history, religious beliefs, and daily life of ancient people.
5. What are the limitations of archaeological sources?
Archaeological sources have some limitations. For example, they can only tell us about the material culture of the past. They cannot tell us about the thoughts, feelings, and experiences of ancient people. Additionally, archaeological sources can be misinterpreted or destroyed.
6. What are the ethical considerations involved in archaeological research?
There are a number of ethical considerations involved in archaeological research. These include:
The need to protect archaeological sites from looting and destruction.
The need to respect the cultural heritage of the communities where archaeological research is conducted.
The need to ensure that the benefits of archaeological research are shared with the communities where it is conducted.
7. What are the future prospects of archaeological research in India?
The future prospects of archaeological research in India are bright. There are many archaeological sites that have yet to be excavated, and new technologies are being developed that can help us to better understand the past.
8. What are some of the challenges facing archaeological research in India?
Some of the challenges facing archaeological research in India include:
The lack of funding for archaeological research.
The lack of trained archaeologists.
The destruction of archaeological sites due to development and natural disasters.
The looting of archaeological sites.
9. What are some of the ways to overcome the challenges facing archaeological research in India?
Some of the ways to overcome the challenges facing archaeological research in India include:
Increasing funding for archaeological research.
Training more archaeologists.
Raising awareness of the importance of archaeological heritage.
Working with communities to protect archaeological sites.
10. What are some of the contributions of archaeological research to our understanding of ancient Indian history?
Archaeological research has made a significant contribution to our understanding of ancient Indian history. It has helped us to:
Reconstruct the material culture of ancient India.
Understand the political history of ancient India.
Learn about the religious beliefs of ancient India.
Gain insights into the daily life of ancient people.
